Pharmaceutical Factories: Inside the World of Drug Production
If you ever wonder where pills, syrups, or creams come from, the answer is the pharmaceutical factory. These plants turn raw chemicals into medicines you can trust. In this guide we break down the main steps, the rules they must follow, and the new ideas shaping the industry today.
How a Drug Plant Turns Ingredients into Medicine
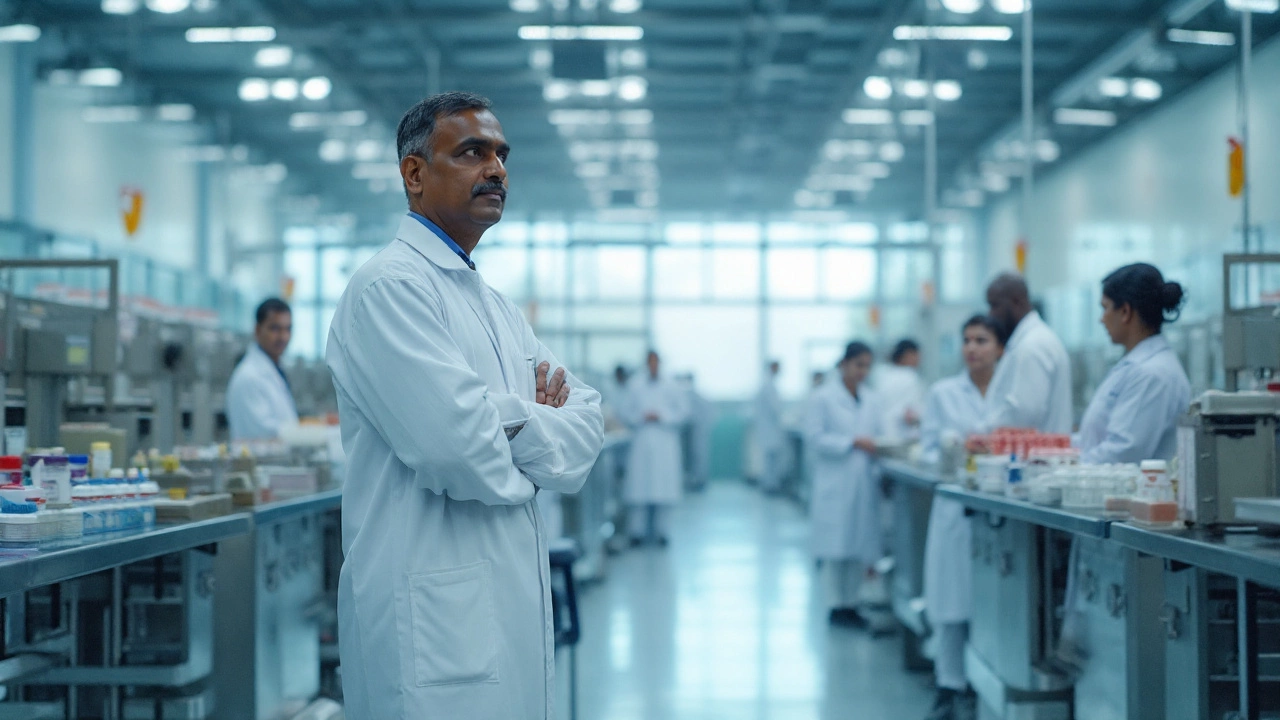
First, the factory receives active ingredients – the chemicals that actually treat a disease. These are mixed with fillers, binders, and sometimes flavors in a big stainless‑steel tank. The mixture is then formed into tablets, filled into capsules, or blended into liquids. Every batch goes through a series of checks: weight, potency, and purity. If anything is off, the batch is stopped before it leaves the building.
After the product is made, it moves to a clean‑room where it is packaged. Packaging isn’t just about looking good; it protects the medicine from light, moisture, and contamination. Labels must list the drug name, dosage, and expiration date, all verified by a separate quality team.
Key Rules That Keep Pharmacies Safe
Pharmaceutical factories operate under strict regulations. In India, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) sets standards for everything from raw material testing to employee hygiene. In the U.S., the FDA does the same. Factories must have a documented quality system, conduct regular audits, and train staff on safety protocols.
One common rule is Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP). GMP means the plant keeps a clean environment, tracks every step, and can prove that each product meets the required quality. If a plant fails an inspection, it can lose its license to sell medicines.
Another safety focus is waste management. Chemical leftovers and water used in cleaning must be treated before they go back into the environment. Many modern factories invest in recycling systems to cut waste and lower costs.
What does all this mean for you? It means that the medicines you buy have passed many checkpoints. When a brand talks about “GMP‑certified” or “FDA approved,” it’s pointing to these protective steps.
Today’s pharmaceutical factories are also getting greener. Some plants use solar panels to run equipment, while others switch to biodegradable packaging. These moves not only help the planet but can also lower production costs, which may reflect in lower prices for patients.
Finally, technology is reshaping the floor. Automation robots handle repetitive tasks, reducing human error. Data analytics monitor temperature, humidity, and equipment performance in real time, alerting staff before a problem grows.
Understanding how a pharmaceutical factory works helps you see why quality and safety are non‑negotiable. Whether you’re a student, a patient, or just curious, knowing the basics lets you make smarter choices about the medicines you trust.
Where Dr Reddy's Drugs Are Made: Inside Their Global Manufacturing Network
Discover exactly where Dr Reddy's medicines are manufactured, how the company maintains quality, and why its global sites matter so much for your health and drug safety.
View More